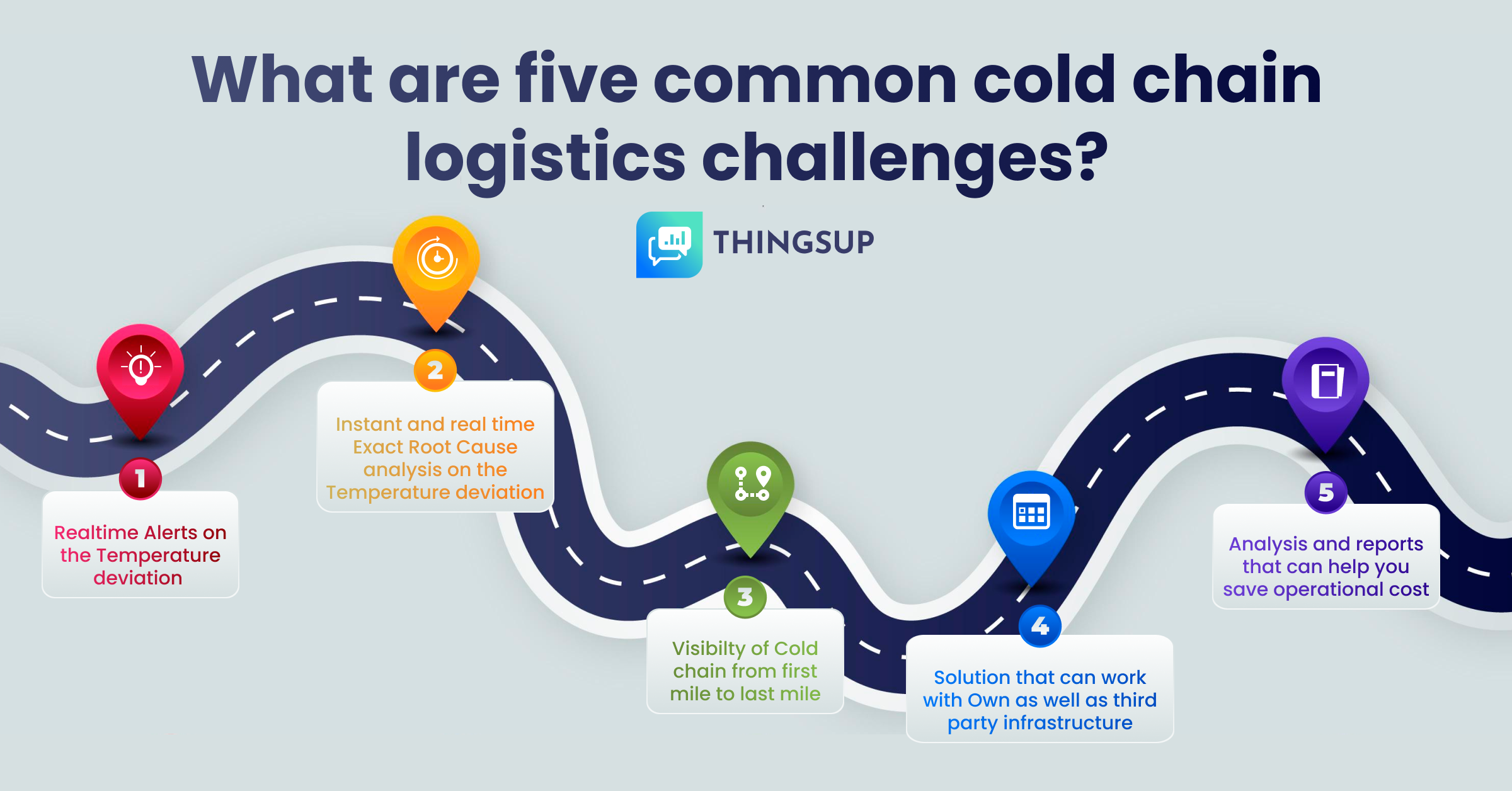
The world of cold chain logistics stands as a crucial pillar in ensuring the safe and efficient movement of temperature-sensitive goods. With a global cold chain market projected to reach $585 billion by 2026, the significance of this industry is undeniable. In this blog, we delve into the intricacies of cold chain logistics, its importance, the mechanics of the cold chain process, and illuminate five of the most common challenges faced in this critical realm.
What Is Cold Chain Logistics?
It involve number of processes involved in transporting, storing, and distributing products that require specific temperature conditions. This intricate ballet of temperature control encompasses a wide array of goods, including perishable foods, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines.
Significance of Cold Chain Logistics:
The importance of cold chain logistics extends far beyond temperature control. It is a linchpin in ensuring product quality, safety, and efficacy. In the pharmaceutical sector, for instance, cold chain logistics ensures that life-saving vaccines and medicines remain potent and effective, safeguarding public health.
How Does the Cold Chain Process Work?
Cold chain logistics involves several interdependent steps, each playing a crucial role in maintaining the desired temperature range:
1. Temperature-Controlled Packaging:
Specialized packaging, such as insulated containers and refrigerated trucks, keeps products within the required temperature range.
For Example, In the food industry, fresh seafood is often transported in insulated containers with gel packs to maintain its cold temperature and quality during transit.
2. Monitoring and Tracking:
Sensors and data loggers continuously monitor temperature and humidity, transmitting real-time data to ensure compliance.
For Example, In the floral industry, sensitive flowers like orchids are equipped with temperature and humidity sensors during transportation, allowing florists to receive real-time data and adjust conditions as needed.
3. Storage and Handling:
Dedicated cold storage facilities maintain consistent temperatures during warehousing and distribution.
For Example, Vaccines in the pharmaceutical sector are stored in dedicated cold storage facilities, like walk-in refrigerators, to ensure consistent temperature control and potency.
4. Transport:
Refrigerated vehicles and containers maintain temperature integrity during transit. Perishable fruits like strawberries are transported in refrigerated trucks to prevent spoilage and maintain freshness throughout their journey from the farm to the grocery store.
5. Last-Mile Delivery:
Ensuring the final stretch of the journey maintains temperature control until the product reaches its destination. Home meal kit services use insulated boxes and ice packs to ensure that ingredients remain at the proper temperature during the final stage of delivery, preserving their quality until they reach the customer’s doorstep.
Major Challenges in Cold Chain Logistics:
Despite its critical role, cold chain logistics faces several formidable challenges:
1.Temperature Fluctuations:
Maintaining consistent temperatures across various stages of the journey is a perpetual challenge. Temperature deviations can lead to product spoilage or reduced efficacy.
2. Regulatory Compliance:
Stringent regulations dictate temperature controls, storage conditions, and reporting standards. Non-compliance can result in legal repercussions.
3.Infrastructure Limitations:
Inadequate cold storage facilities, particularly in developing regions, hinder seamless cold chain operations.
4.Human Error:
Even with advanced technology, human errors during packing, handling, and documentation can compromise the cold chain’s integrity.
5. Cost Pressures:
Operating a robust cold chain incurs substantial costs, from specialized equipment to energy consumption, impacting profit margins.
Trends in Cold Chain Logistics:
The landscape of cold chain logistics is evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer expectations:
1. IoT and Data Analytics:
IoT platform and data analytics offer real-time cold chain monitoring, predictive insights, and visibility into cold chain operations.
2. Sustainability:
Sustainable practices, such as eco-friendly packaging and energy-efficient cold storage, gain traction as environmental concerns grow.
3. Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability, assuring product authenticity and compliance.
4. E-Commerce Surge:
The rise of e-commerce amplifies cold chain complexities, demanding efficient last-mile delivery and personalized temperature control.
Conclusion
The challenges are a constant companion, but with challenges come opportunities for innovation and improvement. To navigate this frosty path successfully, it is imperative to address these challenges with technological advancements, strategic planning, and collaboration. As we continue to rely on cold chain logistics to transport life-saving medicines, fresh produce, and other vital products, it is a shared responsibility to ensure its seamless functioning and constant evolution.
Are you ready to fortify your cold chain logistics strategy? Explore how Thingsup Track cutting-edge solutions can help you overcome challenges and optimize your cold chain operations. Contact us today to embark on a journey towards a more efficient, reliable, and resilient cold chain. Let’s work together to ensure that temperature-sensitive goods reach their destinations safely and with uncompromised quality.