In a world grappling with hunger and scarcity, the paradox of food waste is deeply unsettling. According to a report by the United Nations, nearly one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally.
The pharmaceutical sector is the largest end-user of the cold chain market, accounting for a market share of over 30% in 2022. The food and beverage sector is the second largest end-user, accounting for a market share of over 25%.
In an age where technology and innovation have revolutionized every aspect of our lives, the food industry remains haunted by inefficiencies that result in massive losses.
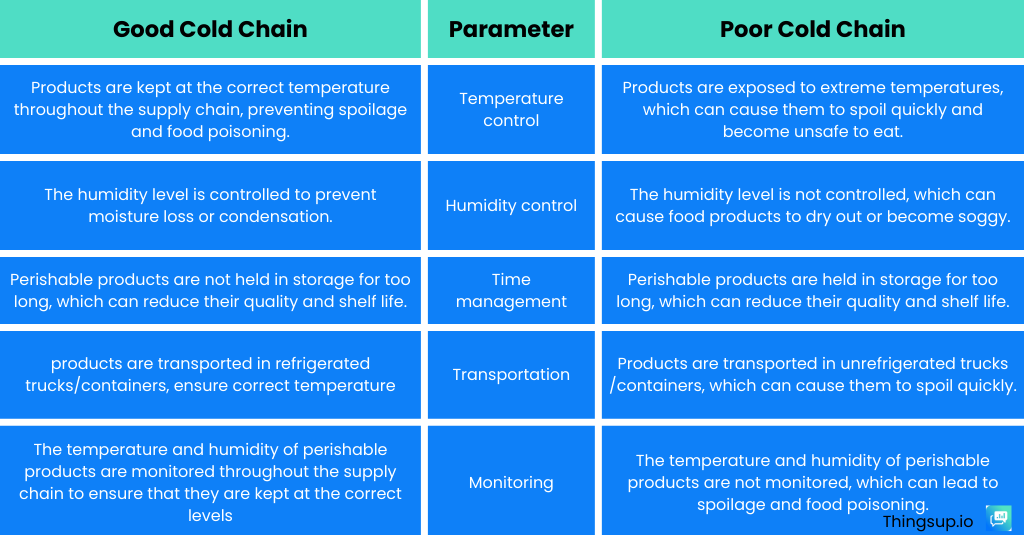
Good Food Cold Chain vs. Poor Food Cold Chain: A Tale of Two Realities
A well-maintained cold chain is akin to a symphony – every note of temperature control, storage, and transportation is carefully orchestrated to preserve the freshness, quality, and safety of perishable goods. On the flip side, a poor cold chain can be likened to a cacophony of waste, where temperature deviations and improper handling lead to spoilage, deterioration, and ultimately, financial losses. Let’s delve into the stark differences between these two realities:
The Significance of a Good Cold Chain for the Food Industry:
The importance of an efficient cold chain in the food industry cannot be overstated. It serves as the guardian of quality, safety, and shelf life for a diverse range of products, from fresh produce to dairy and meat. Here are some key reasons why a good cold chain is vital:
1.Preserving Freshness:
Cold chain management helps to preserve the freshness of food products by preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms. For example, fresh fruits and vegetables can be kept fresh for up to 2 weeks longer when they are stored in a cold chain
2. Extending Shelf Life:
Cold chain management can extend the shelf life of perishable products by up to 50%. This is because cold temperatures slow down the rate of spoilage. For example, milk can be kept fresh for up to 2 weeks longer when it is stored in a cold chain.
3. Minimizing Food Waste:
Cold chain management can help to minimize food waste by ensuring that perishable products are not spoiled before they can be consumed. For example, a study by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations found that cold chain management could reduce food waste by up to 40%
4. Ensuring Food Safety:
Cold chain management helps to ensure food safety by preventing the proliferation of pathogens. Pathogens are microorganisms that can cause foodborne illness. For example, salmonella can grow rapidly in temperatures above 40 degrees Fahrenheit. However, it can be prevented from growing by storing food below 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Introducing Thingsup Cold Chain:
In the quest for an impeccable cold chain, technology emerges as the game-changer. Enter Thingsup Cold Chain, an innovative solution that leverages cutting-edge IoT technology to revolutionize temperature-sensitive logistics:
- Real-Time Temperature Monitoring & analytics:
Thingsup Cold Chain employs sensors and data loggers to provide real-time temperature monitoring at every stage of the supply chain.
2. Custom Alerts and Notifications:
The system sends instant alerts if temperature deviations occur, enabling swift corrective actions and minimizing the risk of spoilage.
3. Data-Driven Insights:
Advanced analytics provide actionable insights into temperature trends, allowing businesses to optimize storage and distribution processes.
4. End-to-End Transparency:
Thingsup Cold Chain ensures transparency by enabling stakeholders to trace the entire journey of a product, from production to consumer.
The consequences of a poor cold chain for the food industry include:
1. Food spoilage: Perishable products can spoil quickly if they are not kept at the correct temperature.
2.Food poisoning: Spoilage can lead to food poisoning, which can cause illness and even death.
3.Food waste: Perishable products that spoil cannot be sold and must be discarded, which is a waste of food and resources.
4.Increased costs: Food spoilage and waste can lead to increased costs for businesses and consumers.
5. Loss of customers: Customers are less likely to do business with companies that sell spoiled or unsafe food.
Conclusion:
The toll of poor cold chain management on the food industry is far-reaching and often underestimated. From financial losses due to spoilage to the perpetuation of global food waste, the consequences are profound. There are many challenges in the cold chain industry, but there is also hope. Technology-driven solutions like Thingsup Cold Chain can help to mitigate losses, preserve quality, and make the food supply chain more sustainable and efficient. By embracing innovation, stakeholders can make a difference.