The rise of air pollution and environmental degradation has led to a global search for ways to reduce vehicular pollution, and Electric vehicles (EVs) are a promising solution, and the Internet of Things (IoT) can help companies improve the performance and customer experience of EVs.
EVs are equipped with sensors that collect data on a variety of performance parameters, such as speed, mileage, battery management, charging, and fault alerts. IoT can be used to collect and analyze this data in real-time to provide better customer experience & performance.
Though the use of IoT in EVs is still in its early stages, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about and use these vehicles.
Electric Vehicle Outlook 2023 by BloombergNEF: This report projects that the global EV market will grow from 6.6 million units in 2022 to 28.1 million units in 2030, at a CAGR of 29%.
Challenges in EV Adoption
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India is facing challenges from government policy, technical limitations, safety concerns, lack of consumer awareness, and inadequate charging infrastructure. The Indian government can address these challenges by providing subsidies for EV buyers, setting stricter emission standards for gasoline and diesel vehicles, investing in research and development to improve the performance and safety of EVs, working with private companies to build more charging stations, and launching public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about the benefits of EVs.
1. Cost :
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is one of the key factors affecting EVs adoption in India. The cost of batteries remains relatively high. This price differential makes EVs less affordable in a price-sensitive market like India.
2. Lack of awareness.
Many Indian consumers are not aware of the benefits of EVs, such as their lower running costs and environmental impact. They may also be concerned about the limited range of EVs and the lack of charging infrastructure. Awareness campaigns can help to address this barrier by educating consumers about the benefits of EVs and how they work. These initiatives can also help to dispel myths about EVs, such as the belief that they are less safe than gasoline-powered vehicles.
3. Range Analysis-
Range anxiety is the fear or uncertainty of running out of battery charge while driving an electric vehicle (EV). There are a few reasons why range anxiety is a barrier to EV adoption in India.
First, the average range of EVs in India is still relatively low, compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. Second, the charging infrastructure in India is not as developed as in some other countries, making it difficult for EV drivers to find places to charge their vehicles. Third, some consumers may be concerned about the reliability of EV batteries and the potential for them to run out of power unexpectedly.
4. Charging infrastructure
Limited charging infrastructure is a major barrier to the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India. The charging infrastructure in India is still not well-developed, especially in non-metro cities and rural areas. This makes it difficult for EV drivers to find places to charge their vehicles, which can be a major inconvenience.
There are a few reasons why the charging infrastructure in India is not as developed as in some other countries. First, the government has not yet put in place enough incentives to encourage businesses to invest in charging infrastructure. Second, the cost of setting up charging stations is relatively high. Third, there is still a lack of awareness about EVs among the general public.
5. Time to charge
Charging time is a major barrier to the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India. The charging time of an EV can be much longer than the refueling time of a gasoline-powered vehicle
Reasons why charging time is a barrier, first is that the average charging time for an EV is still relatively long, compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. Second, the charging infrastructure is not as developed as in some other countries, making it difficult for EV drivers to find places to charge their vehicles quickly. Third, some consumers may be concerned about the reliability of EV batteries and the potential for them to take a long time to charge.
6. Battery & infrastructure challenges
The cost of batteries is still relatively high, and India has limited domestic manufacturing capabilities for batteries, relying mostly on imports. This makes EVs more expensive than gasoline-powered vehicles, which can be a barrier for many consumers.
In addition, the charging infrastructure in India is not as developed as in some other countries. This makes it difficult for EV drivers to find places to charge their vehicles, which can be a major inconvenience.
7. Safety Concern
There are some safety risks associated with EV batteries, such as thermal runaways and fire incidents. These risks need to be addressed in order to gain consumer trust in EVs.
The government can play a role in addressing safety concerns by establishing stringent safety standards and regulations for EVs, charging infrastructure, and battery manufacturing. The government can also collaborate with international organizations and research institutions to develop comprehensive safety guidelines and best practices.
IoT For EV Monitoring & Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) is playing an increasingly important role in electric vehicles (EVs). IoT devices can be used to collect data on the performance of EVs, such as their battery health, driving patterns, and location. This data can be used to improve the efficiency of EVs, optimize their charging, and prevent problems.
For example, IoT devices can be used to monitor the battery health of an EV and send alerts when the battery needs to be replaced. They can also be used to track the driving patterns of an EV and optimize its charging schedule. This can help to extend the range of an EV and reduce the cost of charging.
IoT devices can also be used to improve the safety of EVs.
For example, they can be used to monitor the temperature of the battery and send alerts if it gets too hot. They can also be used to track the location of an EV and send alerts if it is stolen.
Overall, IoT is playing an increasingly important role in the development of EVs. It is helping to make EVs more efficient, safer, and convenient to use.
Here are some specific examples of how IoT is being used in electric vehicles:
1. Battery monitoring:
IoT devices can be used to monitor the health of EV batteries and send alerts when they need to be replaced. This can help to prevent battery failure and extend the life of the battery.
2. Charging optimization:
IoT devices can be used to optimize the charging schedule of an EV based on its driving patterns. This can help to extend the range of the EV and reduce the cost of charging.
3. Safety monitoring:
IoT devices can be used to monitor the temperature of EV batteries and send alerts if they get too hot. This can help to prevent fires and explosions.
4. Location tracking:
IoT devices can be used to track the location of an EV. This can be useful for fleet managers and for recovering stolen vehicles.
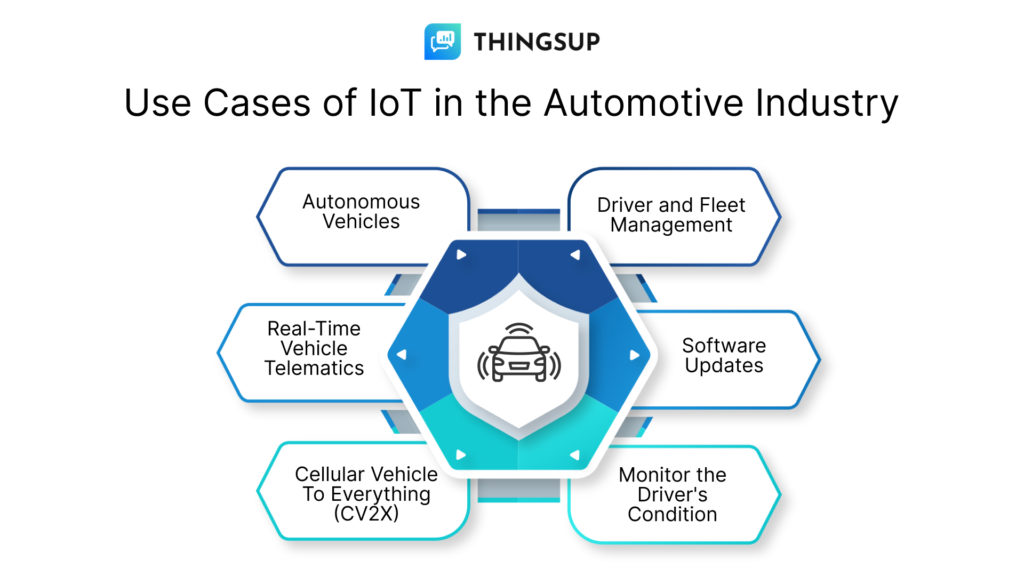
IoT use cases
Here are some of the key use cases of IoT in the automotive industry:
1. Fleet management:
IoT can be used to track and monitor fleets of vehicles, which can help to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
For example, IoT devices can be installed in vehicles to track their location, fuel consumption, and maintenance status. This data can be used by fleet managers to optimize routes, improve fuel efficiency, and schedule maintenance more effectively.
2.Vehicle diagnostics:
IoT can be used to collect data on vehicle performance, which can help to identify and diagnose problems early on. For example, IoT sensors can be installed in vehicles to monitor engine temperature, tire pressure, and other critical systems. This data can be used by mechanics to diagnose problems before they cause a breakdown.
3. Driver assistance systems:
IoT can be used to develop driver assistance systems that can help to prevent accidents. For example, IoT sensors can be used to monitor the driver’s attention and to detect objects in the road ahead. This data can be used to automatically apply the brakes or warn the driver of a potential collision.
4. In-vehicle entertainment and infotainment:
IoT can be used to provide passengers with a more personalized and engaging in-vehicle experience. For example, IoT devices can be used to control the car’s climate system, play music, or access information about the surrounding area.
5. Remote vehicle access:
IoT can be used to give drivers remote access to their vehicles. For example, drivers can use a smartphone app to lock or unlock their doors, start the engine, or check the fuel level. This can be useful for situations where the driver is not near their vehicle, such as when they are running late for work or when they are parked in a remote location.
6. Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication:
IoT can be used to enable V2V communication, which allows vehicles to exchange information with each other. This information can be used to prevent accidents, improve traffic flow, and optimize fuel efficiency. For example, vehicles can use V2V communication to warn each other of upcoming hazards, such as a stalled vehicle or a construction zone.
7. Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication:
IoT can be used to enable V2I communication, which allows vehicles to exchange information with infrastructure, such as traffic lights and road sensors. This information can be used to improve traffic flow, optimize fuel efficiency, and provide drivers with real-time information about their surroundings. For example, vehicles can use V2I communication to receive information about traffic conditions ahead, such as road closures or accidents.
Thingsup Track
Make your Electric Vehicles, Chargers, Batteries, and swapping stations connected and IoT enabled. With ThingsUp you can give your customers a connected experience and monitor, and control your EV infrastructure remotely from Anywhere.
EV Fleet management, EV fleet Rental management, Charger Management, Connected BMS, and IoT Instrument cluster are no longer a hassle with Thingsup.
Benefits of Thingsup Track
1.Comprehensive vehicle analytics is the process of collecting, storing, and analyzing data from a vehicle’s sensors and other systems. This data can be used to provide insights into the vehicle’s performance, health, and usage.
Comprehensive vehicle analytics include:
- Improved vehicle performance: By analyzing data on driving habits, fuel consumption, and other factors, comprehensive vehicle analytics can help drivers improve their driving efficiency and save money on fuel.
- Increased vehicle safety: By monitoring the vehicle’s health and detecting potential problems early on, comprehensive vehicle analytics can help prevent accidents.
- Enhanced customer experience: By providing drivers with insights into their vehicle’s performance, comprehensive vehicle analytics can help improve the customer experience.
2. Comprehensive fleet overview is a system that provides real-time visibility into the status of a fleet of vehicles. It can track the location, speed, and fuel level of each vehicle, as well as other key metrics such as driver behavior and vehicle health. This information can be used to improve fleet efficiency, safety, and compliance.
3. BMS analytics is the process of collecting, storing, and analyzing data from a battery management system (BMS). This data can be used to provide insights into the battery’s health, performance, and usage.
4. Performance analytics for BMS and batteries is the process of collecting, storing, and analyzing data from a battery management system (BMS) and the battery itself. This data can be used to provide insights into the performance, health, and usage of the battery
5. Remote EV parameter modifications are the changes that can be made to the settings or parameters of an electric vehicle (EV) remotely, without the need to physically access the vehicle. This can be done through a cellular connection or a dedicated network.
6. Reports that can be customized to the specific needs of the user. This can include filtering the data, changing the presentation of the data, and adding or removing elements from the report.
7. End User application – Simplified user signup is a process that makes it easy for users to sign up for a service or app. Downloading apps from the app store or play store. Creating an account with simply mobile based registration. OTP based verification & Adding your vehicle(s) to the app, either by scanning the QR code or entering the VIN number. Making the steps more intuitive.Sharing your vehicles with family members, if desired.
8. The vehicle data available on fingertips includes the battery percentage, last updated time, total kilometers driven, current real-time location, speed, and many more. This data can be accessed from a mobile app, which can be downloaded from the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store.
9. The trip planning feature allows users to plan their trips based on the charge available in the vehicle’s battery. This feature can be integrated with turn-by-turn navigation to provide users with an accurate estimate of the time and distance to their destination, as well as the estimated remaining battery charge when they arrive.
10. Geofence and alerts are features that can be used to monitor the location and status of a vehicle. Geofences are virtual boundaries that can be set around specific locations, such as a home or workplace. When a vehicle enters or leaves a geofence, an alert can be sent to the user.
Electric vehicles offer a number of environmental benefits over traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. They produce zero emissions, which means that they do not contribute to air pollution or climate change. They also use less energy, which can save money on fuel costs.
Conclusion
The automobile industry is undergoing a major transformation, with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing adoption of connected and autonomous vehicles. IoT is playing an increasingly important role in this transformation, enabling new and innovative applications that are improving the efficiency, safety, and convenience of vehicles.