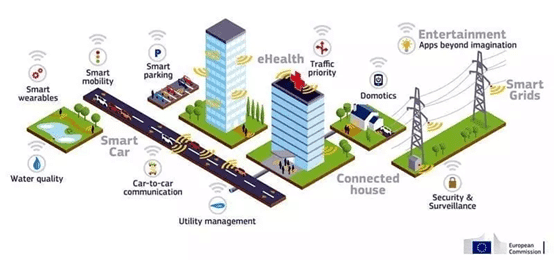
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, two acronyms have been making waves in recent years: 5G and IoT. The fifth generation of wireless technology (5G) and the Internet of Things (IoT) have garnered immense attention, promising transformative changes in the way we connect, communicate, and live. In this blog, we will embark on a journey to explore the intersection of 5G and IoT, their current status, challenges, applications, and their profound impact on shaping the future of our digital world.
According to Ericsson’s recent Mobility Report, there is a significant surge expected in the number of 5G smartphone subscriptions worldwide, reaching approximately 600 million by the end of this year. This figure is nearly triple the total seen in 2020. Additionally, the report predicts that by 2022, the number of 5G subscriptions will surpass the one-billion mark.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is poised to connect over 50 billion devices by 2030, promising a highly interconnected digital ecosystem. What makes this even more remarkable is that 5G networks will be approximately ten times faster than the current LTE networks. This substantial increase in speed will empower IoT devices to communicate and share data faster and more efficiently than ever before.
In the realm of business-to-business sales of IoT devices, it is projected that by 2030, a total of 44.8 million 5G Internet of Things (IoT) units will be sold. Of these units, nearly half are expected to be utilized in Industry 4.0 applications, often referred to as smart factories. The second-largest segment of projected sales in 5G IoT units is expected to be in use cases related to smart cities, with a figure of 8.4 million units.
Among the various IoT segments, connected cars are set to become the largest in the global 5G Internet of Things (IoT) endpoint market. By 2023, it is anticipated that connected cars will hold an installed base market share of 39 percent, equivalent to approximately 19 million endpoints. The overall installed base of 5G IoT endpoints is projected to grow significantly, expanding from 3.5 million in 2020 to an estimated 49 million worldwide by 2023.
This remarkable growth in the adoption of 5G technology is expected to have a significant economic impact. The industry that stands to benefit the most economically is information and communications, with an estimated contribution of around $251 billion to the U.S. GDP between 2021 and 2025. Additionally, the real estate and business services industries are forecasted to contribute $190 billion and $187 billion, respectively, to the economy in the next five years.
Now that we have a comprehensive understanding of the potential of IoT in 5G technologies, let’s delve into a detailed exploration of the advantages that IoT and 5G bring to the table.
The Impact of 5G on the Internet of Things
5G technology is not merely an incremental improvement over its predecessors; it represents an important shift in wireless communication. With significantly higher data speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive device connectivity, 5G opens up a world of possibilities for IoT applications.
- Ultra-High Data Speeds: The theoretical maximum data speed of 5G is 20 gigabits per second (Gbps) up to 100 times faster than 4G, enabling real-time data transmission for IoT devices. This is invaluable for applications like autonomous vehicles and telemedicine.
- Ultra-Low Latency: With latency reduced to a mere millisecond, 5G ensures that IoT devices can communicate instantaneously. This is critical for applications like remote surgery and augmented reality.
- Massive Device Connectivity: It supports up to 1 million devices per square kilometer, making it the ideal infrastructure for connecting the vast array of IoT devices that will be part of our future.
Challenges in IoT & 5G
While the promise of 5G for IoT is undeniable, it comes with its share of challenges.
1.Cost of Deployment:
Rolling out 5G infrastructure is an extremely large undertaking that requires substantial investments from network providers.
2. Security Concerns:
With more devices connected, the attack surface for cyber threats increases. Ensuring robust security measures is paramount.
3. Interoperability:
As IoT devices come from various manufacturers, ensuring interoperability across devices and networks can be complex.
4. Privacy:
The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices raises concerns about data privacy and how that data is utilized.
5.Regulatory Compliance:
IoT applications often involve sensitive data and may need to comply with various regulations, adding complexity to deployments.
5G Applications for IoT
5G and IoT are a powerful combination that can be used to create new and innovative applications across industries.
1. Healthcare:
5G-powered IoT enables remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and efficient healthcare management.
2. Smart Cities:
5G enhances urban infrastructure by enabling smart traffic management, waste management, and public safety solutions.
3. Agriculture:
IoT sensors connected via 5G can optimize farming practices, improve crop yields, and conserve resources.
4. Manufacturing:
IoT-powered by 5G can facilitate predictive maintenance, process automation, and real-time quality control in manufacturing plants.
5. Transportation:
Autonomous vehicles rely on the ultra-low latency of 5G for real-time decision-making, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Use Case: Smart Manufacturing with 5G and IoT
Imagine a smart manufacturing facility where machines communicate seamlessly with one another, constantly monitoring their performance. With 5G’s low latency and high bandwidth, these machines can make real-time decisions, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production schedules.
IoT sensors on the factory floor collect data on temperature, humidity, and machine vibrations, transmitting it instantly over 5G networks. This data is then analyzed by AI algorithms, ensuring that machines operate at peak efficiency, minimizing downtime, and reducing maintenance costs.
Furthermore, IoT-enabled robots collaborate with human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. Workers wear augmented reality (AR) glasses that provide them with real-time data and instructions. This combination of 5G and IoT transforms the manufacturing process into a highly efficient, responsive, and cost-effective operation.
5G & IoT Future Trends
As we peer into the future, several trends are likely to shape the landscape of 5G and IoT:
1. Edge Computing:
Edge computing will gain prominence, allowing data processing to occur closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making.
2. AI Integration:
Artificial intelligence will play a more significant role in processing and analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, enabling smarter and more autonomous systems.
3. Standardization:
Efforts to standardize IoT protocols and security measures will intensify to ensure interoperability and enhance security.
4. Private 5G Networks:
Organizations will increasingly deploy private 5G networks to meet their specific IoT needs, providing more control and security.
5. 5G Beyond Urban Areas:
5G’s expansion into rural areas will unlock new possibilities for IoT applications in agriculture and remote industries.
Advantages of IoT in Smart Cities
1. Efficient Resource Utilization:
IoT enables smart cities to optimize resource usage, such as energy, water, and transportation, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
2. Enhanced Public Services:
IoT-powered smart cities can deliver improved public services, including healthcare, education, and public safety, enhancing the quality of life for residents.
3. Sustainability:
By reducing energy consumption, promoting renewable energy sources, and minimizing waste, IoT contributes to making cities more sustainable and resilient.
4. Economic Growth:
Smart cities attract businesses, create job opportunities, and improve the efficiency of existing industries, driving economic development.
Conclusion
The convergence of 5G and IoT is heralding an era of unprecedented connectivity and innovation. With faster data speeds, lower latency, and massive device connectivity, 5G empowers IoT to reach its full potential. While challenges like cost, security, and privacy persist, the possibilities are boundless. From healthcare and smart cities to manufacturing and transportation, the symbiotic relationship between 5G and IoT promises to transform industries and enrich the lives of individuals worldwide. As we continue on this technological journey, we can anticipate a future where the digital and physical worlds seamlessly merge, unlocking new opportunities and addressing challenges we’ve yet to imagine.