With the rise of IoT platforms and devices, security concerns are also rising. Cybercriminals constantly develop new methods to get into systems, damage reputations, and steal money.
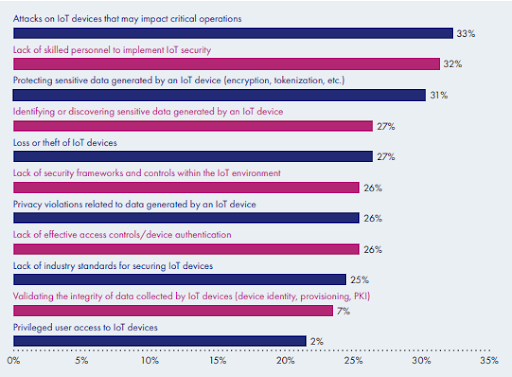
According to the Thales Group
- “Attacks on IoT devices that impact critical operations” is the number one IoT-related security concern.
- “No organization is immune from data security threats, with 49% of global respondents experiencing a data breach at some point.”
- According to their survey, 34% of respondents focus on data security, which averages just 15% of the overall IT security budget.
Among the people who participated in Thales group’s survey, 99% are worried about the security of IoT data.
(source: Thales Group Survey)
IoT platforms can be vulnerable and pose risks to billions of linked devices, a significant issue. Protecting data, devices, and networks from attacks and unauthorized entry requires making sure that IoT platforms are safe.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the essential security measures that IoT platforms should adopt to minimize risks and strengthen security.
Core Security Measures for IoT Platforms
Device Security
- Secure Boot Process: By using a safe boot process, you can ensure that devices will only run software you know you can trust. Thus, harmful code can’t run during the startup process, keeping the device safe from the start.
- Firmware and Software Updates: It is crucial to maintain gadget firmware and software up-to-date to address vulnerabilities and enhance functionality. Subsequently, employing automated update systems ensures devices consistently operate with the latest and most secure versions, reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Remote Device Management: IoT platforms should have remote device management features that allow managers to monitor, configure, and troubleshoot devices safely. As a result, any issues can be resolved quickly without physical access, maintaining the device’s security and functionality.
Data Security
- Data Encryption (in transit and at rest): Encrypting data while sending and keeping sensitive information private and inaccessible to unauthorized people. This prevents information theft and unauthorized modification.
- Access Controls and Authorization: Regularly testing and auditing IoT systems helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Consequently, this proactive approach allows for timely mitigation of risks, ensuring the platform’s resilience.
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Following data protection rules, like GDPR and CCPA, is essential to keep user data safe and ensure compliance with legal requirements. This ensures that the platform handles personal data responsibly and avoids legal penalties.
- Measures to stop data loss: Taking steps to prevent data loss, like regular backups and duplication, ensure that data is always available and correct. It prevents data from getting lost when hardware fails, hackers attack, or something else goes wrong.
Network Security
- Protocols for safe communication: Secure communication methods like HTTPS, TLS, and MQTT over TLS encrypt and protect data sent between platforms and devices. It stops monitoring and data theft while the communication is going on.
- Firewall Protection: Deploying firewalls is essential for filtering and monitoring network traffic. Consequently, they prevent unauthorized access and safeguard against external threats. In essence, firewalls create a protective barrier separating trusted and untrusted networks, ensuring the platform’s security.
- Enhancing Security with Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) is crucial for quickly identifying and addressing potential security breaches. The IDPS system carefully monitors network traffic for any signs of suspicious activity. It then immediately takes necessary measures to prevent any possible attacks.
Platform Security
- Secure Authentication and Authorization: Safeguard the IoT platform by implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong authorization mechanisms. It ensures that only authorized users are granted access.
- Role-Based Access Control: Establishing clear roles and permissions for users and devices is essential for efficiently managing access to IoT resources. In particular, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a crucial security measure that restricts user access to only the resources required for their roles. As a result, potential security risks are mitigated, and a more secure environment is established.
- Vulnerability Management: You can reduce potential security risks by regularly checking for flaws and applying patches and updates promptly. Proactive vulnerability management fixes vulnerabilities before their exploitation.
- Incident Response Plan: Creating an incident response plan is essential. Sticking to this plan ensures structured and effective handling of security incidents, minimizing their impact. An incident response plan clearly outlines how to handle security breaches and return to normal afterward.
Security by Design
- Importance of Integrating Security from the Development Phase: Integrating security features from the start is crucial. It ensures they become an integral part of the IoT platform. This proactive method helps identify security risks early in the development process, thus minimizing them.
- Threat Modeling and Risk Assessment: Threat modeling helps identify potential security threats. Subsequently, risk assessments determine the proper defenses to implement. This organized approach ensures that safety measures prioritize the most severe threats.
- Secure Coding Practices: Secure coding techniques can significantly reduce software code vulnerabilities. As a result, secure coding builds the platform to resist potential security threats, lowering the attack risk.
Final Thoughts
We know that IoT platform usage is increasing. Therefore, strong security measures are crucial to protect against emerging risks and vulnerabilities. Implementing comprehensive security for devices, data, networks, and platforms is crucial. It reduces IoT platform vulnerability to security risks. Adding security from the beginning of the development process and following best practices for ongoing testing and monitoring strengthen overall security.