If the innovations that modern technology is bringing are used properly, not just businesses but our planet can also prosper. The work to save the planet has intensified as global temperature rises and the climate changes.
Today, governments and industries worldwide are coming forward together to win the race for net zero emissions. In this case, IoT is one such technology that has emerged quite well.
With the help of IoT platforms, steps are being taken towards achieving zero-emission, which is a very positive sign.
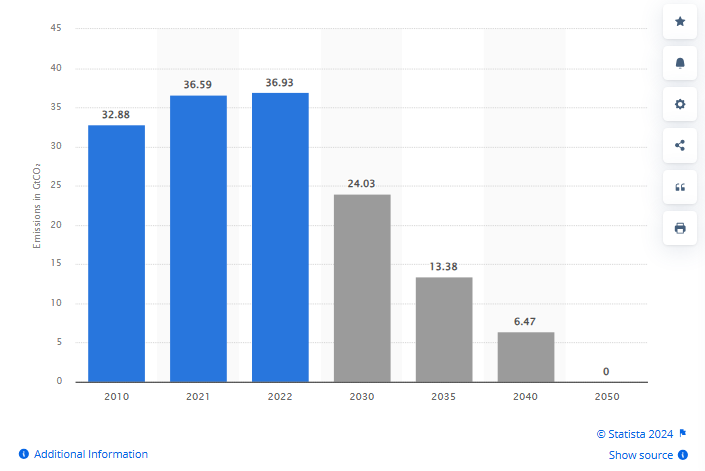
Here is the report by Statista on Projected total carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions worldwide in the Net Zero Scenario from 2010 to 2050.
IoT connects platforms, systems, devices, and data streams to create a network that optimises operations and transforms them to a new level.
However, IoT technology is not just about operational efficiency; but also a powerful technology that helps companies address challenges to reduce their environmental impact. IoT provides actionable insights and solutions that help businesses achieve sustainability while growing from energy consumption to integration of renewable energy sources.
This blog will discuss how IoT technology helps companies achieve their net-zero goals and make them competitive in this highly competitive world.
Understanding Net Zero and Its Importance
Net zero emission means removing the same amount of greenhouse gases released into the environment by vehicles, industries, or other means. Overall, returning from the environment, the same percentage of greenhouse gases enter the environment and balance the entire environment.
These measures are essential for
- To reduce global warming and extreme climate events.
- To comply with international agreements such as the Paris Agreement and COP-26.
- To conduct business keeping consumer preferences in mind while following sustainable practices.
Global emissions data show that sectors such as energy production, manufacturing, and transportation contribute 25%, 21%, and 14% of emissions respectively.
To reduce the impact of these contributors, businesses are moving towards advanced technologies like IoT for sustainable transformation.
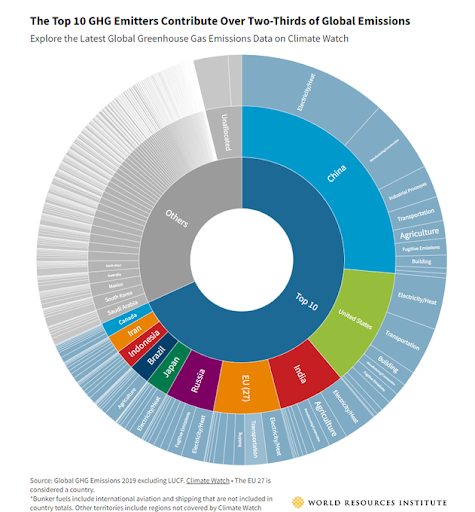
And here are the top 10 GHG emitters contributing over two-thirds of global emissions ,according to the World Resources Institute.
How IoT Enables Net Zero Emissions?
Real-Time Energy Monitoring
IoT tracks energy consumption across every facility in an organization, providing real-time insights into usage patterns. From machinery to lightning systems, IoT sensors collect this data and send it to centralized dashboards for further analysis. This data shows how much energy is being used, which operations are being used, and in which areas optimizations can be made.
For example, during non-operational hours, automated systems can power down unnecessary equipment, significantly cutting energy wastage.
According to a report, companies that integrate IoT energy management solutions can save up to 20% on energy costs. And this also makes a difference to the environment, reducing CO₂ emissions.
In addition, IoT monitoring platform use predictive analytics that help the organizations understand historical trends and easily predict future energy demands. As global energy demand grows, IoT will ensure businesses can reduce their carbon footprints without sacrificing productivity.
Smart Grid Optimization
IoT technology transforms the power grid into smart, self-regulating systems. These systems can improve energy efficiency on a broader level. Traditional power grids suffer from this by not balancing energy supply and demand, which greatly increases the chances of energy wastage.
Here, IoT sensors help the grids by providing real-time data on energy consumption, grid loads, and renewable energy availability.
Smart grids automatically optimize energy distribution. These optimize the utilization of renewable energy such as solar and wind power by balancing demand and supply. During peak hours, IoT systems can predict demand spikes in advance and redirect energy from low demand areas to high demand areas. It also helps in reducing the reliance on fossil fuels.
According to reports, implementing IoT in grid systems can reduce energy losses by 15% and increase renewable energy usage by 30%.
Decarbonizing Transportation with IoT
Transportation contributes to approximately 14% of global emissions. If we talk about IoT platforms, they prove to be a great help in transportation and have the ability to reduce energy emissions. They offer smart mobility systems ranging from fleet optimization to electric Vehicle optimization.
Fleet optimization includes IoT enabled GPS trackers and fuel monitoring systems that improve route efficiency. They avoid congested routes and suggest routes to drivers that consume less fuel and reduce pollution.
IoT provides a real-time battery monitoring system for EVs that allows energy to be used efficiently. This improves the performance of the vehicle and makes it last longer.
Smart parking systems using IoT technology reduce the time vehicles spend idling which further reduces emissions.
Apart from this, IoT supports connected public transportation systems which get real-time updates which improves scheduling. These systems reduce dependency on private vehicles, decreasing overall emissions.
Industrial Automation and Predictive Maintenance
Industries have the biggest contribution in global emissions. Here IoT optimises operations through automation and predictive maintenance which can reduce energy wastage. IoT systems optimize machinery in such a way that the machines minimise unnecessary energy usage.
Predictive maintenance uses IoT sensors to continuously monitor equipment health, which helps know about equipment failure in advance. This can reduce unexpected downtime.
IoT driven smart factories can optimize operations by integrating robotics, AI and realtime analytics which makes them energy efficient and eligible to contribute towards net zero goals.
Renewable Energy Integration
IoT optimises renewable energy usage so that it can be used more efficiently. Sensors installed in wind turbines, solar panels and hydroelectric systems monitor their performance so that their performance can be further optimised over time and maximum energy output can be obtained.
For example, IoT systems can predict weather patterns to determine when renewable sources like wind and power will be most productive. Using this data, organizations can plan better for their energy storage and grid distribution. Besides, by properly using renewable energy sources, IoT devices can reduce organizations’ dependence on fossil fuels.
The solar energy sector, with IoT integration, has reported a 15% increase in efficiency, reducing costs and emissions.
Precision Agriculture
About 10% of the world’s emissions come from agriculture, mostly due to the overuse of water and fertilizer.
This can be reduced by IoT-powered precision agriculture. This technology is able to make the best use of available resources. IoT sensors closely analyze the weather and crop health and tell how much water and fertilizer to apply.
For example, a farm that used an IoT irrigation system cut its water usage by 25%. This saved money on energy costs from pumping and reduced methane emissions from runoff. IoT also helps in the automated monitoring of livestock, which improves feeding schedules and cuts down on waste.
Apart from reducing emissions, these new ideas also increase crop yields, which ensures there is enough food for everyone.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
IoT improves the efficiency and monitoring of carbon capture and storage technologies. IoT sensors track the CO2 levels in the capture system. The point is to ensure that the system is operating with optimal performance and safety.
In addition, IoT also provides real-time monitoring of CO2 storage sites so that if there is any leakage in the system, it can be detected. This increases transparency and accountability throughout the system for emission reduction efforts.
For example, using IoT systems, direct air capture facilities can see how much CO2 is being removed and run their operations more smoothly. When connected to the internet, carbon capture and storage (CCS) can store billions of tons of CO2 each year, making net-zero goals that much closer to reality.
Challenges in Implementing IoT for Net Zero
Yes, it is true that IoT has a lot of potentials to drive net zero initiatives, but there are also many challenges in implementing it properly. Companies that want to use it should understand these barriers and take appropriate steps.
1. High Initial Investment
Your starting cost to deploy IoT systems will be higher. You will have to spend initially on upgrading hardware, software and infrastructure. Businesses have to integrate IoT sensors, gateways and connectivity solutions across all their facilities. All this becomes difficult for small and medium sized enterprises due to the higher costs.
For example, if we talk about the renewable energy sector, installing IoT-enabled solar and advanced wind monitoring systems requires advanced equipment and skilled labor. And for organizations with limited budgets, it becomes difficult to make this higher investment in the long term.
2. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
IoT relies on continuous data collection. During this data collection, many sensitive operations take place. As this vast data is transmitted across the network, the chance of a breach is very high.
This requires companies to invest in robust cybersecurity measures that include everything from encryption, secure protocols to regular system updates. This makes IoT deployment complex. Also, it can be hard to follow data privacy laws like GDPR or CCPA, especially for organisations that work with people all over the world.
3. Infrastructure and Connectivity Issues
IoT requires reliable internet connectivity and robust infrastructure. And if your business is in remote areas where connectivity is not as required, many issues can arise.
Moreover, integrating IoT technology into existing infrastructure is time consuming and expensive. Here companies face many challenges in scaling their IoT operations as there are few chances of IoT compatibility issues with legacy systems.
4. Complexity in Integration
Oftentimes, issues arise when IoT systems are integrated with existing processes and technologies. Here, businesses must ensure that IoT devices, IoT platforms and apps work harmoniously together.
For example, integrating IoT sensors into manufacturing processes may involve reconfiguring machinery and workflows. This complexity demands skilled personnel, which may not always be available and can result in delays or operational disruptions during the transition period.
5. Data Overload and Management
IoT generates a huge amount of data, which brings up the issue of data overload. Analyzing and effectively managing this data is important to gain actionable insights. This raises the question of how to manage data overload? All these things require tools. On the other side, companies often lack the tools or expertise to process this information, which results in underutilized resources.
6. Standardization and Interoperability
Uniform standards for the IoT ecosystem are not set, so there is a possibility of interoperability issues between devices and platforms. Now, if you deal in IoT systems from multiple vendors, each vendor’s IoT solution may be different, here, integrating diverse IoT systems can be a logistical nightmare.
For example, If a business uses IoT sensors from different vendors, they might have trouble with compatibility. In this case, standardisation is very important so that devices can talk to each other easily.
Conclusion
The journey towards Net-Zero emissions is tough but essential. Here, IoT has emerged as an excellent technology. From optimizing energy use to integrating renewables and from revolutionizing transportation to industrial operations, IoT platform have performed exceptionally well. It is no secret that IoT has bridged the gap between technological advancement and environmental sustainability.
But there are a few problems along the way. These are the problems with cost, complexity, and standardization that need new ideas, teamwork, and dedication. The Internet of Things (IoT) is not just a technology; it is a key part of a sustainable future.
As the world moves towards a greener tomorrow, IoT brings great hope. The hope is to achieve sustainability while staying in competition.